Hair Growth Rate and Phases (Anagen, Catagen, Telogen)
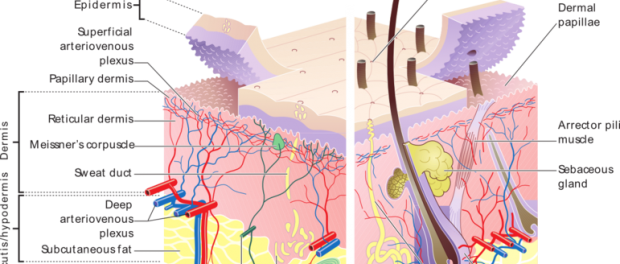
Human hairs are elongated strands primarily composed of the protein keratin. The main function of hair is to provide warmth, both by acting as an insulator on the surface and by standing erect in cold and windy conditions to slow down the flow of air on the skin surface. It may also offer some degree of protection, albeit minimal compared to other structures in the body like the bones, and helps to trap dust particularly when it is located at the entrance of cavities. The hair follicle and shaft along with the erector pili muscle that moves it and the sebaceous gland that empties into the shaft is known as the pilosebaceous unit. It is believed that some chemicals in the oily sebum secreted from these glands adhere to the hair follicle and shaft and may contribute to odors that could play a part in attraction. For humans though, hair plays an integral part in the aesthetic features, be it the hair on the head, eyebrows or even torso. Hair Anatomy A strand of hair broadly has two parts, the follicle which lies under the skin and originates from the bulb, and the shaft. The hair shaft has 3 layers … Continue reading Hair Growth Rate and Phases (Anagen, Catagen, Telogen)