Can Gum Disease Be Reversed with Proper Care?
Can gum disease be reversed? Learn how early gum damage heals, what stops progression, and the steps to restore gum health.
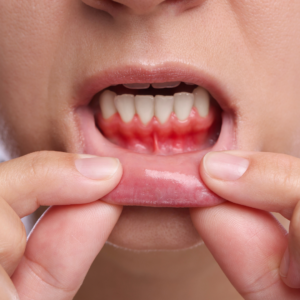
It’s easy to panic when your gums bleed during brushing or feel swollen and tender. Most people immediately assume this means permanent gum damage or tooth loss. That fear is completely understandable because gum disease often progresses silently. The good news is that gum disease does not always lead to irreversible harm. In fact, when caught early, it can be fully reversed. And even in more advanced stages, it can still be controlled and stabilized. This article explains exactly what can be reversed, what cannot be reversed, and the steps that restore gum health based on the latest dental and periodontal science.Dental Cavities, Tooth Decay Causes, Prevention and Treatment – Healthhype
Gum Disease Basics
Gum disease begins when plaque, a sticky bacterial film, builds up along the gumline. If it stays on the teeth too long, the gums respond with inflammation. This inflammation is your body’s attempt to defend itself, but over time it can become destructive. Gum disease exists on a spectrum. The earliest stage is gingivitis, which affects only the gum tissue and does not involve bone loss. Gingivitis is the only stage that can be fully reversed. When inflammation is not addressed, it progresses into periodontitis, a more advanced condition where bone and connective tissue begin to break down. Once the disease reaches this point, it can no longer be reversed entirely, though it can be treated and controlled to prevent further deterioration.
The difference between gingivitis and periodontitis matters because most people only seek treatment once symptoms become impossible to ignore. However, the early stage often produces mild signs—slight bleeding when brushing, puffiness, or bad breath. This is why consistent oral care and regular dental visits are critical. Gum disease rarely improves on its own. If plaque is not removed, the bacteria within it multiply and produce toxins that irritate gum tissue, making the inflammation progressively worse.
Gingivitis Explained
Gingivitis is considered the reversible stage of gum disease. At this point, the damage is limited to gum inflammation without any destruction of the bone supporting the teeth. Gingivitis develops when plaque accumulates and begins irritating the gums. You might notice small signs such as bleeding during brushing, swollen gums, mild tenderness, or persistent bad breath. These symptoms appear because the immune system is reacting to bacteria along the gumline.
Even though these symptoms can be alarming, gingivitis can heal completely when proper steps are taken. Professional cleaning removes hardened plaque (tartar) that brushing and flossing can’t eliminate. Once the irritants are removed, the gums typically begin to heal within days. Most people can reverse gingivitis within two weeks with consistent at-home care, which includes brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and cleaning the gumline thoroughly.Prevent Tooth Decay Gingivitis Effectively – Healthhype
The speed of recovery depends on how consistently plaque is removed. When oral hygiene is irregular, bacteria quickly recolonize, and the inflammation returns. That is why gingivitis is often described as a daily battle between plaque formation and plaque removal. The earlier you intervene, the more successful the reversal.
Periodontitis Stages
If gingivitis is ignored, the inflammation spreads deeper into the tissues supporting the teeth. At this point, the disease becomes periodontitis, and the damage is no longer completely reversible. Periodontitis progresses through several stages. In the earliest stage, the gums detach slightly from the teeth, forming small pockets where bacteria thrive. As inflammation continues, the bone supporting the teeth begins to break down. In moderate periodontitis, these pockets deepen, and bone loss becomes more noticeable. In severe periodontitis, significant bone destruction occurs, teeth may shift or loosen, and gum recession becomes visible.
The crucial point is that although periodontitis cannot be reversed, it can be treated and stabilized. Dentists use deep-cleaning procedures such as scaling and root planing to remove bacteria from deep pockets. This allows the gums to heal and reattach to the tooth surface. With long-term maintenance, patients can stop the disease from progressing further. However, bone lost during periodontitis does not naturally grow back without specifically planned surgical procedures.Preventing Cavities: Essential Tips for Everyone – Healthhype
Reversing Gum Disease
When asking whether gum disease can be reversed, the answer depends on the stage. Gingivitis is fully reversible. Periodontitis is not, but it can be managed extremely well. In gingivitis, the tissues are inflamed but intact. Professional cleaning and consistent oral care typically restore the gums to complete health. If a person eliminates plaque consistently, the inflammation disappears, bleeding stops, and the gums regain their healthy, firm texture.Does Fluoride Really Protect Teeth? – Healthhype
Periodontitis, however, causes permanent damage to the bone and connective tissues holding the tooth. Treatment can stop progression and sometimes help the gums reattach slightly, but the original architecture cannot be restored without periodontal surgery. Even with surgery, bone regeneration is limited. Still, with regular deep cleanings, lifestyle changes, and excellent daily hygiene, people with periodontitis can maintain their teeth for many years.
Oral Hygiene Role
Oral hygiene plays the most important role in reversing early gum disease. Healthy gums depend on consistent mechanical removal of plaque. Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste ensures that bacteria do not accumulate long enough to irritate the tissues. A soft-bristled brush angled toward the gumline helps lift plaque that settles along the edges of the gums. Flossing removes bacteria between teeth where toothbrushes cannot reach. When flossing is neglected, plaque hardens into tartar within twenty-four to forty-eight hours, and tartar cannot be removed at home.
People with early gum disease often notice dramatic improvements simply by brushing longer and more gently, cleaning the entire gumline, and flossing daily. Mouthwashes containing antibacterial agents can also help reduce the bacterial load. While mouthwash alone cannot reverse gum disease, it supports the healing process.
Professional Treatments
Professional dental care is necessary for reversing gingivitis and managing periodontitis. Dentists perform scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline. When tartar is removed, the gums begin to heal and inflammation reduces. Some cases require adjunctive treatments such as localized antibiotics or antimicrobial rinses to control bacteria within deep pockets.
Laser therapy is another option used by some dentists to shrink gum pockets and promote healing. Although not a replacement for traditional methods, it can enhance treatment outcomes. For advanced periodontitis, surgical procedures may be needed. Flap surgery allows dentists to clean deep areas more thoroughly. Bone grafts, gum grafts, and guided tissue regeneration can help rebuild areas damaged by periodontitis, though the results vary by individual case.
Reversing Early Gum Disease
The problem many people face is that early gum disease produces symptoms they ignore. Bleeding during brushing, bad breath, and occasional gum tenderness are easy to dismiss, especially when there is no pain. This can lead to the agitation stage of disease—when inflammation deepens, plaque hardens into tartar, and the gums pull away from the teeth. At this point, the damage becomes harder to reverse.
The solution is early intervention. When gingivitis is detected early, a professional cleaning combined with improved daily habits can restore gum health quickly. People who commit to consistent brushing and flossing usually see that bleeding stops, breath improves, and swelling reduces within one to two weeks. Hydration, reduced sugar intake, and avoidance of smoking also support the healing process. With consistent care, early gum disease does not become permanent.
Periodontitis Management
Although periodontitis cannot be reversed, it can be kept under control for a lifetime. Management focuses on stopping the progression of bone loss. Deep cleanings are usually recommended every three to four months, far more frequently than routine cleanings. This helps prevent bacteria from recolonizing the gum pockets. Patients are taught specific cleaning techniques and tools suitable for their level of gum recession. Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or immune disorders, is also essential because these conditions accelerate gum disease.
Stabilizing periodontitis prevents tooth loss, improves comfort, and reduces inflammation throughout the body. Chronic gum disease can increase systemic inflammation, so controlling it can also support general health. HealthHype provides resources on related systemic issues, such as body-wide inflammation (https://healthhype.com/inflammation-causes-symptoms-and-treatment.html) and immune system disorders (https://healthhype.com/immune-system-disorders-types-symptoms-treatment.html), which can indirectly affect gum health.
Diet and Lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle have a major influence on gum healing. Foods rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals support the immune system and help tissues recover from inflammation. Leafy greens, berries, citrus fruits, and foods rich in omega-3 fats help reduce gum irritation. The oral microbiome also benefits from probiotics found in yogurt and fermented foods. Conversely, smoking dramatically increases the risk of gum disease and slows healing. Alcohol overuse and frequent sugary snacks also contribute to plaque buildup and worsen inflammation.
Hydration plays a significant role as well. Saliva is a natural defense against harmful oral bacteria. When the mouth is dry, bacteria flourish and plaque forms more quickly. Drinking water regularly supports the natural cleansing mechanisms in the mouth.
Oral Bacteria Impact
The bacteria responsible for gum disease, including Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythia, thrive in environments where plaque is left undisturbed. These bacteria release toxins that trigger inflammation. When plaque hardens into tartar, it forms a rough surface that allows bacteria to anchor firmly and spread. This is why tartar removal is essential during dental cleanings. If left untreated, the bacterial toxins seep deeper into tissue, damaging ligaments and bone. Periodontal treatments aim to disrupt these bacterial colonies and reduce the inflammatory burden on gum tissue.
Risk Factor Awareness
Certain individuals are more prone to gum disease than others. Smoking is the most significant risk factor because it weakens gum tissue and hides symptoms such as bleeding. People with diabetes have an increased risk due to higher inflammation levels and reduced healing capacity. Hormonal changes during pregnancy, explained in more detail on HealthHype (https://healthhype.com/pregnancy-hormones-changes-and-symptoms.html), can also increase gum sensitivity and bleeding. Genetics, nutritional deficiencies, immune disorders, and chronic dry mouth contribute to the risk as well. Understanding these risk factors helps patients and dentists design personalized prevention plans.6 Reasons And Remedies For Persistent Bad Breath – Healthhype
Home Remedies Guide
Home remedies can support gum healing when combined with professional care. Warm saltwater rinses soothe swollen gums and reduce bacteria. Oil pulling, although not a replacement for brushing, can help decrease the bacterial load. Aloe vera gel and clove oil have natural anti-inflammatory properties and can offer temporary comfort. Green tea contains antioxidants that protect tissues from oxidative stress. These remedies complement, but do not replace, brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings.Does Fluoride Really Protect Teeth? – Healthhype
Preventing Gum Disease Progression
Preventing gum disease requires consistency. Brushing two to three times daily, flossing at least once, and using fluoride products are essential. Regular dental visits ensure plaque and tartar are managed professionally. Managing systemic conditions and maintaining a nutrient-rich diet contribute to healthy gums. Avoiding tobacco, moderating alcohol, staying hydrated, and reducing sugar intake significantly reduce the risk of gum damage. Prevention is far easier than treatment. Once gums lose bone support, maintenance becomes a lifelong commitment.
For conditions like chronic bad breath, which often accompanies gum disease, HealthHype offers additional insights here: https://healthhype.com/bad-breath-halitosis-causes-and-treatment.html. For gum disease tied to dental infections, more information is available here: https://healthhype.com/tooth-infection-signs-symptoms-treatment.html.
External References
American Dental Association: https://ada.org
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Oral Health: https://cdc.gov/oralhealth
Mayo Clinic – Periodontal Disease Overview: https://mayoclinic.org
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research: https://nidcr.nih.gov
Cleveland Clinic – Gum Disease Information: https://my.clevelandclinic.org