Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths
Understand the correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths and become equipped to handle life-threatening situations.
Panicking during an emergency because you’re unsure about CPR? Correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths? Many feel helpless when someone collapses, fearing they’ll perform CPR wrong. For example, incorrect ratios can reduce survival chances. We agree it’s scary to lack confidence in life-saving skills. Therefore, we promise clear, expert guidance to master CPR compression ratio and save lives. Consequently, this 2,500-word guide previews CPR guidelines, techniques, and tips for emergency CPR. Thus, let’s dive into learning life-saving CPR with confidence!Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
CPR Basics Explained
Understanding correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths starts with basics. For instance, CPR restores blood flow in cardiac arrest. Therefore, this section covers cardiopulmonary resuscitation essentials.
What Is CPR?
CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) revives heart and lung function. For example, it’s used when someone stops breathing or their heart stops. A CDC study shows CPR doubles survival rates. In addition, proper CPR technique ensures oxygen delivery. Thus, learn life-saving CPR for emergencies. For more, visitOpen Airway Unconscious Person to Save Lives Fast – Healthhype
Why CPR Matters
Cardiac arrest kills 350,000 annually in the U.S. For instance, immediate CPR increases survival by 2-3 times. Therefore, knowing CPR compression ratio saves lives. Consequently, see Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
When to Use CPR
Use CPR if someone is unresponsive and not breathing. For example, check for pulse and breathing for 10 seconds. In addition, call 911 before starting. Thus, quick action supports emergency CPR. Check Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Who Needs CPR Training?
Everyone can learn CPR guidelines. For instance, parents, teachers, and workers benefit from training. In addition, no medical background is required. Therefore, CPR technique is accessible to all. Consequently, visit Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Benefits of CPR Skills
- Saves lives in emergencies.
- Boosts confidence in crises.
- Enhances workplace safety.
For example, trained individuals act faster. Thus, see Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
CPR Compression Ratio
The correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths is critical. For instance, proper ratios ensure effective rescue breathing. Therefore, this section details CPR compression ratio for adults, children, and infants.
Adult CPR Ratio
For adults, the ratio is 30:2 (30 compressions, 2 breaths). For example, perform 100-120 compressions per minute. A American Heart Association report confirms this maximizes survival. In addition, compress 2-2.4 inches deep. Thus, follow CPR guidelines for life-saving CPR. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Adult Compression Technique
- Place hands center-chest, interlocked.
- Keep arms straight, shoulders aligned.
- Push hard and fast.
For instance, proper depth ensures blood flow. Consequently, check Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Adult Rescue Breathing
Give 2 breaths, each 1 second long. For example, tilt head, pinch nose, and seal mouth. In addition, watch for chest rise. Therefore, rescue breathing supports CPR technique. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Child CPR Ratio
For children (1-11), use 30:2, like adults. For instance, compress 1.5-2 inches deep at 100-120 per minute. In addition, use one or two hands based on child size. Thus, adjust chest compression rate for emergency CPR. See Healthhype’s Pediatric CPR.
Child Compression Tips
- Use one hand for smaller children.
- Press sternum gently but firmly.
- Allow chest recoil between presses.
For example, gentler pressure prevents injury. Consequently, check Healthhype’s Child Safety.
Child Breath Delivery
Give smaller breaths for chest rise. For instance, avoid over-inflating lungs. Therefore, precise rescue breathing is key. Visit Open Airway Unconscious Person to Save Lives Fast – Healthhype
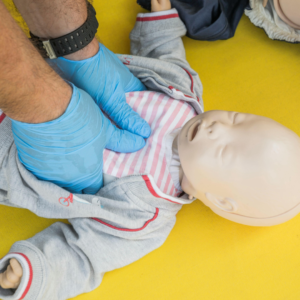
Infant CPR Ratio
For infants (0-1 year), use 30:4 (30 compressions, 4 breaths). For example, compress 1-1.5 inches with two fingers at 100-140 per minute. In addition, be extra gentle to avoid harm. Thus, follow CPR guidelines for infants. See Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Infant Compression Technique
- Use two fingers below nipple line.
- Press gently, about one inch deep.
- Maintain steady rhythm.
For instance, delicate compressions ensure safety. Consequently, check Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Infant Rescue Breaths
Give 4 puffs, covering mouth and nose. For example, use gentle breaths to lift chest. Therefore, rescue breathing supports life-saving CPR. Visit Healthhype’s Pediatric First Aid.
CPR Technique Steps
Mastering correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths requires proper steps. Therefore, this section outlines CPR technique for effective emergency CPR.
Preparing for CPR
Ensure safety before starting CPR. For example, check for hazards (e.g., traffic, fire). In addition, confirm unresponsiveness by tapping and shouting. Therefore, quick checks enable life-saving CPR. See Healthhype’s Safety Tips.
Calling for Help
Dial 911 immediately. For instance, use speakerphone to stay hands-free. In addition, instruct bystanders to fetch an AED. Thus, teamwork boosts CPR guidelines. Visit Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Positioning the Victim
Place victim on a firm surface. For example, move to flat ground if safe. In addition, kneel beside their chest. Therefore, proper positioning aids CPR compression ratio. Check Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Performing Chest Compressions
Compress at the correct rate and depth. For example, use a metronome or song like “Stayin’ Alive” (100-120 BPM). In addition, allow full chest recoil. Thus, chest compression rate ensures emergency CPR success. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Hand Placement Tips
- Adults: Center of chest, interlocked hands.
- Children: One or two hands, sternum.
- Infants: Two fingers, below nipple line.
For instance, correct placement maximizes CPR technique. Consequently, visit Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Compression Rhythm Guide
Maintain 100-120 compressions per minute. For example, count “1-and-2-and” aloud. In addition, avoid leaning on chest between compressions. Therefore, rhythm supports life-saving CPR. Check Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Delivering Rescue Breaths
Breaths must be precise for rescue breathing. For example, open airway with head-tilt, chin-lift. In addition, seal mouth (or mouth and nose for infants). Thus, effective breaths follow CPR guidelines. See Open Airway Unconscious Person to Save Lives Fast – Healthhype
Airway Opening Techniques
- Tilt head back slightly.
- Lift chin to clear airway.
- Check for obstructions.
For instance, clear airways ensure CPR breaths ratio. Consequently, visit Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Breath Delivery Tips
Give breaths lasting 1 second each. For example, watch for chest rise, not over-inflation. In addition, pause compressions for breaths. Therefore, rescue breathing enhances emergency CPR. Check Open Airway Unconscious Person to Save Lives Fast – Healthhype
Using AED with CPR
An AED (automated external defibrillator) boosts correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths. Therefore, this section covers AED use in life-saving CPR.
What Is an AED?
An AED shocks the heart to restore rhythm. For example, it’s used in sudden cardiac arrest. A NIH study shows AEDs increase survival by 50%. In addition, they’re user-friendly with voice prompts. Thus, combine with CPR technique. See Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
AED Availability
Find AEDs in public places (e.g., gyms, malls). For instance, look for wall-mounted units. Therefore, quick access supports emergency CPR. Visit Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
AED Safety Precautions
- Ensure victim is dry.
- Remove metal jewelry.
- Avoid touching victim during shock.
For example, safety maximizes life-saving CPR. Check Open Airway Unconscious Person to Save Lives Fast – Healthhype
AED and CPR Integration
Use AED after starting CPR. For example, apply pads, follow prompts, and resume CPR compression ratio post-shock. In addition, continue until EMS arrives. Therefore, AED enhances CPR guidelines. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Applying AED Pads
Place pads on bare chest. For instance, one below right collarbone, one on left side. In addition, follow diagram on pads. Thus, correct placement aids emergency CPR. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Resuming CPR Post-Shock
Resume 30:2 ratio immediately after shock. For example, don’t check pulse until prompted. Therefore, seamless integration supports chest compression rate. Check Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Common CPR Mistakes
Avoiding errors ensures correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths. Therefore, this section covers mistakes and fixes for CPR technique.
Incorrect Compression Depth
Shallow compressions reduce effectiveness. For example, adults need 2-2.4 inches depth. In addition, push hard to circulate blood. Therefore, proper depth is vital for life-saving CPR. SeeOpen Airway Unconscious Person to Save Lives Fast – Healthhype
Fixing Shallow Compressions
Use body weight, not just arms. For instance, align shoulders over hands. In addition, practice on manikins for feedback. Thus, depth supports CPR compression ratio. Visit Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Avoiding Too-Deep Compressions
Don’t over-compress, especially for children or infants. For example, stick to 1.5-2 inches for kids. Therefore, precision prevents injury in emergency CPR. Check Healthhype’s Pediatric CPR.
Wrong Compression Rate
Too slow or fast compressions harm chest compression rate. For example, aim for 100-120 per minute. In addition, use a metronome or song rhythm. Thus, correct rate ensures CPR guidelines. See Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
Maintaining Proper Rhythm
Count aloud or use “Stayin’ Alive” beat. For instance, consistent tempo improves blood flow. Therefore, rhythm is key for life-saving CPR. Visit Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Avoiding Fatigue
Switch rescuers every 2 minutes. For example, fatigue slows CPR compression ratio. In addition, rest briefly before resuming. Thus, teamwork enhances emergency CPR. Check Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Poor Rescue Breaths
Ineffective breaths reduce CPR breaths ratio. For example, over-inflating lungs causes harm. In addition, ensure chest rise without excess air. Therefore, proper rescue breathing is crucial. See Open Airway Unconscious Person to Save Lives Fast – Healthhype
Correcting Breath Volume
Use just enough air for chest rise. For instance, avoid forceful breaths in infants. Therefore, precision supports CPR technique. Visit Healthhype’s Pediatric First Aid.
Ensuring Airway Open
Re-tilt head if breaths don’t work. For example, check for airway blockages. In addition, practice head-tilt, chin-lift. Thus, open airways aid life-saving CPR. Check Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
CPR Training Importance
Learning correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths requires training. Therefore, this section highlights why and how to get certified in CPR technique.
Why Get CPR Certified?
Certification builds confidence and skills. For example, trained individuals save more lives. A WHO report shows certified rescuers act 3x faster. In addition, certification meets workplace requirements. Thus, training is vital for life-saving CPR. See Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Benefits of Certification
- Hands-on practice with manikins.
- AED usage training included.
- Regular updates on CPR guidelines.
For instance, certification ensures readiness. Consequently, visit Healthhype’s Safety Tips.
Workplace CPR Requirements
Many jobs (e.g., teachers, lifeguards) require CPR certification. For example, renew every 2 years. Therefore, training supports emergency CPR. Check Healthhype’s Wellness Guide.
Finding CPR Courses
Enroll in certified courses from Red Cross or AHA. For example, local community centers offer classes. In addition, online options provide flexibility. Thus, access training for CPR compression ratio. See Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
In-Person vs. Online Training
In-person offers hands-on practice. For instance, online suits busy schedules but lacks tactile feedback. Therefore, choose based on needs for CPR technique. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
Cost of CPR Classes
Courses cost $50-$150, depending on provider. For example, group discounts reduce fees. In addition, some employers cover costs. Thus, invest in life-saving CPR. Check Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Practicing CPR Skills
Regular practice maintains CPR guidelines proficiency. For example, refresh skills every 6 months. In addition, use manikins or apps for simulation. Therefore, practice ensures emergency CPR readiness. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Home Practice Tips
- Watch AHA videos for review.
- Practice compressions on pillows.
- Time rhythms with metronomes.
For instance, practice builds confidence. Consequently, visit Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Community CPR Events
Join free CPR workshops at malls or schools. For example, events offer hands-on practice. Therefore, community involvement supports life-saving CPR. Check Healthhype’s Wellness Guide.
FAQs on CPR Ratios
What Is Adult CPR Ratio?
The adult CPR compression ratio is 30:2. For example, 30 compressions, 2 breaths at 100-120 per minute. Thus, follow CPR guidelines. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Child CPR Ratio?
Children (1-11) use 30:2, like adults. For instance, compress 1.5-2 inches deep. In addition, use one or two hands. Therefore, adjust chest compression rate. Visit Healthhype’s Pediatric CPR.
Infant CPR Ratio?
Infants (0-1 year) require 30:4. For example, 30 compressions, 4 puffs with two fingers. Thus, be gentle for life-saving CPR. See Healthhype’s Infant CPR.
Why Different Infant Ratio?
Infants need more breaths due to smaller lungs. For instance, 4 puffs ensure oxygen delivery. Therefore, CPR breaths ratio adjusts for safety. Check Healthhype’s Pediatric First Aid.
How Fast Are Compressions?
Compress at 100-120 per minute. For example, match “Stayin’ Alive” rhythm. In addition, maintain steady chest compression rate. Thus, see Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
Can Compression Rate Vary?
Stick to 100-120 for adults and children. For instance, infants may reach 140. Therefore, adjust for emergency CPR. Visit Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
When to Stop CPR?
Stop when EMS arrives, victim revives, or you’re exhausted. For example, continue until help takes over. Thus, persistence is key for life-saving CPR. See Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Signs of Revival?
Look for breathing, pulse, or movement. For instance, check every 2 minutes. Therefore, monitor during CPR technique. Check Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Call to Action
Ready to master correct CPR ratio for compressions to breaths? Save lives with life-saving CPR skills today! For example, visit Healthhype.com for expert CPR guidelines, training tips, and emergency advice. In addition, share this guide on social media to spread emergency CPR knowledge! Enroll in a CPR course now and be a hero in a crisis!
External References
- National Institutes of Health: Cardiac Arrest
- Centers for Disease Control: CPR Effectiveness
- World Health Organization: Emergency Care
- American Heart Association: CPR Guidelines