When to Use AED in ABCD Process
Explore the critical moments of when to use AED in ABCD process and improve your emergency response skills dramatically.
Panicking during a cardiac emergency because you’re unsure about AED use? When to use AED in ABCD process? Many feel overwhelmed, fearing they’ll miss critical steps in a crisis. For example, delayed or incorrect AED use can reduce survival chances. We agree it’s terrifying to lack confidence in life-saving skills. Therefore, we promise clear, expert guidance to master AED in emergency within the ABCD framework. Consequently, this 2,500-word guide previews ABCD process CPR, AED timing, and tips for cardiac arrest response. Thus, let’s dive into saving lives with life-saving AED!Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
ABCD Process Overview
Understanding when to use AED in ABCD process starts with the ABCD framework. For instance, ABCD guides emergency response. Therefore, this section explains ABCD process CPR essentials.
What Is ABCD?
ABCD stands for Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation. For example, it’s a structured approach for cardiac arrest. A CDC study shows ABCD doubles survival rates. In addition, it integrates CPR with AED. Thus, master emergency CPR steps for life-saving AED. See Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Purpose of ABCD
ABCD restores heart and lung function. For instance, it ensures oxygen delivery to vital organs. Therefore, ABCD process CPR saves lives. Consequently, check Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
When to Use ABCD
Apply ABCD for unresponsive, non-breathing victims. For example, check pulse and breathing for 10 seconds. In addition, call 911 immediately. Thus, quick action supports cardiac arrest response. Visit Healthhype’s Safety Tips.
Who Needs ABCD Training?
Anyone can learn ABCD process CPR. For instance, parents, teachers, or workers benefit from training. In addition, no medical background is required. Therefore, AED usage guide is accessible to all. See Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Benefits of Training
- Boosts confidence in emergencies.
- Improves survival outcomes.
- Enhances workplace safety.
For example, trained individuals act faster. Consequently, visit Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Community Impact
Trained responders strengthen communities. For instance, more ABCD-trained people increase survival rates. Thus, training supports life-saving AED. Check Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
AED Role Explained
Knowing when to use AED in ABCD process depends on AED function. For instance, AEDs restore heart rhythm. Therefore, this section covers automated external defibrillator basics.
What Is an AED?
An AED delivers electric shocks to restart the heart. For example, it’s used in sudden cardiac arrest. A NIH study shows AEDs boost survival by 50%. In addition, voice prompts guide users. Thus, AEDs are vital for heart rhythm shock. See Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
AED Accessibility
AEDs are in public places like airports or gyms. For instance, look for wall-mounted units with clear signs. Therefore, quick access aids AED in emergency. Visit Healthhype’s Safety Tips.
AED Safety Features
- Analyzes heart rhythm automatically.
- Delivers shocks only when needed.
- Provides step-by-step instructions.
For example, safety ensures effective life-saving AED. Check Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Why Use AED?
AEDs correct ventricular fibrillation, a chaotic heart rhythm. For instance, CPR alone can’t always restart the heart. A American Heart Association report shows AEDs triple survival odds. Therefore, CPR with AED is critical. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
AED vs. CPR Alone
CPR maintains blood flow; AED fixes rhythm. For example, combining both maximizes survival. Thus, cardiac arrest response relies on AED usage guide. Visit Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Survival Rate Impact
Immediate AED use raises survival to 70%. For instance, every minute delay drops odds by 10%. Therefore, timing is key for life-saving AED. Check Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
AED for Different Ages
AEDs are safe for adults and children over 1. For example, use pediatric pads for kids 1-8 years. In addition, avoid AEDs on infants under 1 without specific pads. Thus, adjust for emergency CPR steps. See Healthhype’s Pediatric CPR.
Pediatric AED Use
Pediatric pads reduce shock strength. For instance, follow AED prompts for child settings. Therefore, proper use ensures AED in emergency safety. Visit Healthhype’s Child Safety.
ABCD Process Steps
Mastering when to use AED in ABCD process requires clear steps. Therefore, this section outlines emergency CPR steps with AED in emergency.
Airway: Open the Airway
Check and clear the airway first. For example, tilt head back and lift chin. In addition, remove visible obstructions. A WHO report stresses airway management. Thus, open airways support ABCD process CPR. See Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Head-Tilt, Chin-Lift Method
- Gently tilt head backward.
- Lift chin to open airway.
- Check for breathing (5-10 seconds).
For instance, correct technique ensures oxygen flow. Consequently, visit Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
Clearing Obstructions
Use finger sweep for visible objects. For example, avoid blind sweeps to prevent choking. Therefore, clear airways aid cardiac arrest response. Check Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Breathing: Check for Breathing
Assess breathing for 5-10 seconds. For instance, look for chest rise or listen for breaths. In addition, if absent, start CPR. Thus, breathing checks guide emergency CPR steps. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Signs of No Breathing
- No chest movement.
- No breath sounds.
- Blue lips or face.
For example, these signal immediate action. Therefore, ABCD process CPR begins. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Rescue Breaths Delivery
If trained, give 2 breaths after 30 compressions. For example, each breath lasts 1 second. In addition, ensure chest rises. Thus, breaths support life-saving AED. Check Healthhype’s Pediatric CPR.
Circulation: Start Compressions
Perform 30 compressions at 100-120 per minute. For example, press 2-2.4 inches deep for adults. In addition, allow full chest recoil. Therefore, CPR with AED maintains circulation. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Compression Technique Tips
- Interlock hands, center-chest.
- Keep arms straight, shoulders aligned.
- Push hard and fast.
For instance, proper depth ensures blood flow. Consequently, visit Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Maintaining Compression Rhythm
Match “Stayin’ Alive” rhythm (100-120 BPM). For example, count “1-and-2-and” aloud. In addition, use a metronome if available. Thus, steady cardiac arrest response supports AED in emergency. Check Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
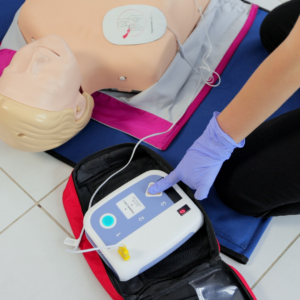
Defibrillation: Apply AED
Use AED as soon as it’s available. For example, apply pads, follow prompts, and shock if advised. A NIH study shows early defibrillation saves lives. Therefore, when to use AED in ABCD process is step D. See Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
AED Pad Placement
- Right pad: Below collarbone.
- Left pad: Below left nipple.
- Follow pad diagrams.
For instance, correct placement ensures heart rhythm shock. Visit Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
Delivering AED Shock
Clear victim before shock (“Stand clear!”). For example, resume CPR immediately post-shock. In addition, follow AED prompts. Thus, seamless life-saving AED use is key. Check Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Post-Shock CPR Resumption
Resume 30:2 ratio after shock. For example, don’t check pulse until prompted. Therefore, quick CPR supports emergency CPR steps. Visit Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
AED Timing Guidelines
Precise timing for when to use AED in ABCD process is critical. Therefore, this section details AED usage guide for cardiac arrest response.
When to Use AED?
Apply AED after confirming no pulse or breathing. For example, start CPR, then use AED when available. In addition, aim for within 3-5 minutes. Thus, early use boosts life-saving AED. See Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
AED After CPR Start
Perform CPR (30:2) for 2 minutes if alone. For instance, attach AED during compression pause. Therefore, CPR with AED maximizes survival. Visit Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Bystander AED Retrieval
Instruct others to fetch AED immediately. For example, say, “Get the AED now!” to save time. In addition, continue CPR while waiting. Thus, teamwork supports emergency CPR steps. Check Healthhype’s Safety Tips.
When to Avoid AED?
Don’t use AED on conscious or breathing victims. For example, check responsiveness first. In addition, avoid wet surfaces or metal contact. Therefore, safety ensures AED in emergency. See Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
AED Contraindications
- Responsive or breathing victims.
- Water or conductive surfaces.
- Infants under 1 without pediatric pads.
For instance, avoid misuse for life-saving AED safety. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Pediatric AED Adjustments
Use pediatric pads for children 1-8 years. For example, adult pads may harm smaller hearts. In addition, follow AED child settings. Thus, adjust for cardiac arrest response. CheckCorrect CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
AED Use Duration
Continue AED until EMS arrives or victim revives. For example, follow prompts every 2 minutes for rhythm checks. In addition, resume CPR if no shock advised. Therefore, persistence aids heart rhythm shock. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Switching Rescuers
Switch CPR roles every 2 minutes to avoid fatigue. For instance, coordinate with AED prompts. In addition, communicate clearly with team. Thus, teamwork supports emergency CPR steps. Visit Healthhype’s First Aid Guide.
Stopping AED Use
Stop when victim shows breathing or pulse. For example, check every 2 minutes per AED prompts. Therefore, monitor during AED in emergency. Check Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Signs of Revival
Look for breathing, movement, or pulse. For instance, pause CPR briefly to check. In addition, continue if no signs appear. Thus, vigilance supports life-saving AED. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Common AED Mistakes
Avoiding errors ensures when to use AED in ABCD process is effective. Therefore, this section covers mistakes and fixes for AED usage guide.
Incorrect Pad Placement
Wrong pad placement reduces heart rhythm shock effectiveness. For example, pads too close or reversed fail. In addition, follow pad diagrams carefully. Therefore, correct placement is vital. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Fixing Pad Placement
- Check diagrams on pads.
- Place firmly on bare skin.
- Shave chest hair if needed.
For instance, precision enhances life-saving AED. Visit Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Ensuring Pad Adhesion
Press pads to ensure contact. For example, remove sweat or water from chest. In addition, dry skin improves adhesion. Thus, good contact supports cardiac arrest response. Check Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Delaying AED Application
Waiting too long lowers survival odds. For example, every minute delay cuts chances by 10%. In addition, apply AED within 3-5 minutes. Therefore, speed is critical for AED in emergency. See Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Avoiding AED Delays
Fetch AED while starting CPR. For instance, delegate retrieval to bystanders. In addition, don’t pause CPR unnecessarily. Thus, quick action ensures CPR with AED. Visit Healthhype’s Safety Tips.
Balancing CPR and AED
Don’t stop CPR to wait for AED. For example, continue 30:2 until AED is ready. In addition, minimize interruptions. Therefore, balance supports emergency CPR steps. Check Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Unsafe AED Operation
Unsafe use risks harm to rescuers or victim. For example, touching victim during shock causes injury. In addition, clear area before shocking. Therefore, safety is key for life-saving AED. See Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
Clearing Before Shock
Shout “Clear!” and check surroundings. For example, ensure no one touches victim. In addition, visually confirm safety. Check Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Avoiding Wet Surfaces
Dry victim’s chest before pad placement. For example, move to dry ground if possible. In addition, wipe off water or sweat. Thus, dry conditions enhance AED in emergency. See Healthhype’s Safety Tips.
Checking for Metal Hazards
Remove jewelry or metal from chest. For instance, metal conducts electricity, risking burns. Therefore, clear hazards support heart rhythm shock. Visit Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
AED Training Importance
Learning when to use AED in ABCD process requires proper training. For instance, training builds life-saving skills. Therefore, this section highlights certification for AED usage guide.
Why Get AED Certified?
Certification ensures confidence and competence. For example, trained users save more lives. A WHO report shows certified rescuers act 3x faster. In addition, certification meets workplace needs. Thus, training is vital for life-saving AED. See Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Certification Benefits
- Hands-on AED practice.
- CPR and AED integration skills.
- Updated ABCD process CPR guidelines.
For instance, certification prepares for emergencies. Consequently, visit First Aid in Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) – Healthhype
Workplace AED Requirements
Jobs like lifeguards or teachers often require certification. For example, renew every 2 years. In addition, employers may fund training. Thus, certification supports cardiac arrest response. Check Healthhype’s Wellness Guide.
Finding AED Courses
Enroll in Red Cross or AHA-certified courses. For example, community centers or hospitals offer classes. In addition, online options provide flexibility. Therefore, access training for AED in emergency. See Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
In-Person vs. Online Courses
In-person offers hands-on practice with AEDs. For instance, online suits busy schedules but lacks tactile feedback. Therefore, choose based on needs for emergency CPR steps. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
Course Costs
Classes cost $50-$150, depending on provider. For example, group discounts may apply. In addition, some workplaces cover fees. Thus, invest in life-saving AED skills. Check Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
Practicing AED Skills
Regular practice maintains AED usage guide proficiency. For example, refresh skills every 6 months. In addition, use AED trainers or apps for simulation. Therefore, practice ensures cardiac arrest response readiness. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Home Practice Tips
- Watch AHA AED tutorial videos.
- Practice pad placement on manikins.
- Simulate scenarios with family.
For instance, practice builds confidence. Consequently, visit Healthhype’s First Aid Training.
Community AED Workshops
Join free AED demos at schools or malls. For example, workshops offer hands-on practice. In addition, network with trained responders. Thus, community events support life-saving AED. Check Healthhype’s Community Safety.
FAQs on AED Use
When to Use AED?
Use AED after confirming no pulse or breathing. For example, start CPR, then apply AED within 3-5 minutes. Thus, early AED in emergency saves lives. See Healthhype’s CPR Guide.
Where Is AED in ABCD?
AED is step D (Defibrillation) in ABCD process CPR. For instance, use after Airway, Breathing, Circulation checks. Therefore, timing is key for heart rhythm shock. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
Can AED Harm Victims?
AEDs are safe if used correctly. For example, they only shock specific rhythms. In addition, avoid use on breathing victims. Thus, safety ensures life-saving AED. See First Aid in Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) – Healthhype
Avoiding AED Misuse?
Check responsiveness before using AED. For instance, don’t apply on conscious people. Therefore, proper checks support cardiac arrest response. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Care.
Is AED Safe for Kids?
Yes, with pediatric pads for ages 1-8. For example, adult pads may harm smaller hearts. In addition, follow child-specific prompts. Thus, adjust for emergency CPR steps. See Healthhype’s Pediatric CPR.
Infant AED Use?
Avoid AED on infants under 1 unless pediatric pads available. For instance, use CPR instead. Therefore, safety is key for AED in emergency. Check Healthhype’s Infant CPR.
How Long to Use AED?
Continue until EMS arrives or victim revives. For example, check rhythm every 2 minutes. In addition, resume CPR if no shock advised. Thus, persistence aids life-saving AED. See Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
When to Stop AED?
Stop if victim shows breathing or pulse. For instance, check during AED pauses. Therefore, monitor for cardiac arrest response. Visit Healthhype’s Emergency Guide.
Call to Action
Ready to master when to use AED in ABCD process? Save lives with life-saving AED skills today! For example, visit Healthhype.com for expert ABCD process CPR tips, AED training, and emergency advice. In addition, share this guide on social media to spread emergency CPR steps knowledge! Enroll in an AED course now and be a hero in a crisis!First Aid in Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) – Healthhype
External References
- National Institutes of Health: Cardiac Arrest
- Centers for Disease Control: CPR and AED Effectiveness
- World Health Organization: Emergency Care
- American Heart Association: AED Guidelines