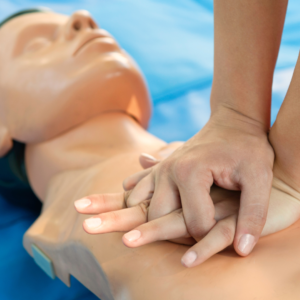
How Long to Check Breathing: Step-by-Step Guide
Discover the critical duration of checking breathing in first aid. Your knowledge could be vital in life-saving situations.
Your Moment to Save a Life
Picture this: someone collapses in front of you, and panic surges through the crowd. In that critical moment, knowing how long to check breathing in first aid can transform you from a bystander into a lifesaver. Every second counts in an emergency, and a quick, accurate breathing check can mean the difference between life and death. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the exact duration to check breathing, step-by-step techniques, common mistakes to avoid, and expert tips to handle emergencies with confidence. Whether you’re a parent, coworker, or concerned citizen, this article equips you with practical, easy-to-understand knowledge to act decisively. Let’s dive into this life-saving skill and prepare you to make a difference!Choking on Mucus (Phlegm, Sputum) Causes – Healthhype
Why Check Breathing?
Checking breathing is the cornerstone of first aid. It’s the first step to determine if someone is alive and what immediate actions are needed, such as CPR or calling for help. A proper breathing assessment timeframe ensures you respond effectively in high-stakes situations.
Life-or-Death Importance
Breathing delivers oxygen to the brain and vital organs. Without it, brain damage can begin within 4–6 minutes, and death can follow shortly after. A quick first aid breathing check identifies whether someone is breathing normally, gasping, or not breathing at all, guiding your next steps. The American Heart Association (AHA) stresses that assessing breathing is critical in emergencies like cardiac arrest or choking.Choking on Mucus (Phlegm, Sputum) Causes – Healthhype
Consequences of Errors
Incorrectly assessing breathing can delay life-saving interventions. For instance, mistaking agonal gasps for normal breathing can prevent timely CPR, worsening outcomes. A precise check breathing time ensures you act swiftly and correctly. Learn more about emergency first aid procedures to understand the broader context.
Building Emergency Confidence
Mastering the evaluate breathing period builds confidence in high-pressure situations. With clear knowledge and practice, you’ll stay calm, assess accurately, and take appropriate action, whether at home, work, or in public.
How Long to Check?
The recommended duration to assess breathing duration in first aid is 10 seconds. This timeframe ensures accuracy without delaying critical actions like CPR or calling emergency services.Choking on Mucus (Phlegm, Sputum) Causes – Healthhype
Official Guidelines
Leading organizations, including the AHA and American Red Cross, recommend checking breathing for no more than 10 seconds. This breathing assessment timeframe allows you to confirm normal breathing, detect agonal gasps, or identify the absence of breathing.
Why 10 Seconds?
Ten seconds is a carefully chosen balance. It’s long enough to observe chest movement, hear breath sounds, or feel air movement, but short enough to avoid delaying life-saving measures like CPR. In emergencies, every second is precious, and this check breathing time optimizes your response.
When to Adjust Timing
While 10 seconds is the standard for most cases, specific scenarios, such as infants or drowning victims, may require slight modifications. We’ll explore these later to ensure you’re prepared for all situations.Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Steps to Check Breathing
A correct first aid breathing check involves more than just timing. Follow these clear, beginner-friendly steps to assess breathing accurately and confidently in an emergency.
Step 1: Ensure Scene Safety
Before approaching, confirm the environment is safe. Avoid hazards like traffic, fire, or electrical dangers. Your safety is crucial to provide effective help. Learn more about first aid safety basics.
Step 2: Check Responsiveness
Gently tap the person’s shoulder and shout, “Are you okay?” If they don’t respond, they’re likely unconscious, signaling the need for an emergency breathing assessment. See unconsciousness first aid for related insights.
Step 3: Look, Listen, Feel
For 10 seconds, use the “look, listen, feel” method:
-
Look for chest rise and fall, a clear sign of breathing.
-
Listen for breath sounds by placing your ear near their mouth and nose.
-
Feel for air movement on your cheek.
This three-step approach ensures you detect even faint breathing during the evaluate breathing period.Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Step 4: Identify Abnormal Breathing
Gasping or irregular breaths, known as agonal breathing, are not normal. Often seen in cardiac arrest, agonal gasps require immediate CPR. Treat them as no breathing to avoid delays.
Step 5: Take Immediate Action
If no breathing is detected after 10 seconds, call emergency services or start CPR if trained. Quick action is critical to restore oxygen flow and prevent brain damage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even well-intentioned responders can make errors during a CPR breathing check. Avoiding these pitfalls ensures your assessment is accurate and effective.Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment – Healthhype
Rushing the Assessment
Checking for less than 10 seconds may cause you to miss subtle signs of breathing. Stay calm, count steadily to 10, and observe carefully to ensure an accurate assess breathing duration.
Misinterpreting Agonal Breathing
Agonal breathing is not effective breathing. These irregular gasps, common in cardiac arrest, are a sign of severe distress. If observed, start CPR immediately. Learn more about cardiac arrest first aid.Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
Delaying Critical Steps
Spending more than 10 seconds on a first aid breathing check delays actions like CPR or calling for help. Stick to the recommended check breathing time to keep your response efficient.
Ignoring Scene Safety
Approaching an unsafe scene risks your safety, preventing you from helping. Always assess the environment before performing an emergency breathing assessment.Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
Overlooking Subtle Signs
Faint breathing or slight chest movement can be easy to miss, especially in noisy or chaotic environments. Focus on the “look, listen, feel” method for the full 10 seconds to avoid errors.
When to Start CPR?
If no normal breathing is detected after your evaluate breathing period, CPR may be necessary to restore oxygen flow. Understanding when to act is critical for life-saving outcomes.
CPR Basics
CPR combines chest compressions and rescue breaths to mimic heart and lung function. It’s used when someone is unresponsive and not breathing normally (or only gasping). Only trained individuals should perform CPR, but everyone should know when it’s needed. Visit HealthHype’s CPR guide for detailed instructions.Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
Signs CPR Is Needed
If the person is unconscious and not breathing normally after a 10-second CPR breathing check, start CPR if trained. If untrained, call emergency services immediately and follow their guidance. The AHA notes that prompt CPR can double or triple survival chances.
Timing and Urgency
Brain damage can begin within 4 minutes without oxygen, and death can occur within 8–10 minutes. Starting CPR quickly during an emergency breathing assessment is critical to prevent irreversible harm.
Special Cases in Breathing Checks
Certain scenarios require tailored approaches to the assess breathing duration. Here’s how to handle them effectively.
Checking Infants
For infants, use a gentler approach during the first aid breathing check. Place your cheek close to their mouth and nose, looking for subtle chest movement. The 10-second rule applies, but be extra cautious to detect faint breaths. Learn more about infant first aid.
Choking Emergencies
If someone is choking, their airway may be blocked, preventing normal breathing. Perform the Heimlich maneuver before checking breathing. After clearing the airway, assess for 10 seconds. See choking first aid.Correct CPR Ratio for Compressions to Breaths – Healthhype
Drowning Victims
After rescuing a drowning victim, check breathing immediately for 10 seconds. If absent, start CPR promptly, as oxygen deprivation is severe. Review drowning first aid.
Hypothermia Cases
In hypothermia, breathing may be slow or faint, making it harder to detect. Check for the full 10 seconds, as subtle signs can be missed. Learn about hypothermia first aid.
Allergic Reactions
Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) can cause breathing difficulties. If breathing is absent or abnormal after 10 seconds, use an epinephrine auto-injector if available and start CPR. See anaphylaxis first aid.
Training and Certification
Formal training enhances your ability to perform a first aid breathing check and respond in emergencies. It’s an investment in saving lives.
Finding First Aid Courses
Organizations like the Red Cross and AHA offer first aid and CPR courses, available online or in-person. These programs cover breathing assessment timeframe, CPR, and other critical skills, suitable for beginners and experienced responders alike.
Benefits of Certification
Certified individuals respond faster and more accurately during an emergency breathing assessment. Certification also boosts workplace safety, community preparedness, and personal confidence in emergencies.
Staying Updated
First aid guidelines evolve, so refresh your skills every 1–2 years to stay aligned with best practices. Stay informed with HealthHype’s first aid updates.
Practice Makes Perfect
Regular practice reinforces the check breathing time and techniques. Role-playing scenarios with friends or family can simulate real emergencies, helping you stay calm and effective under pressure.Stress Gastritis in Critically Ill Patients – Healthhype
Advanced Tips for Experts
For those with first aid experience, refining your evaluate breathing period skills can enhance your effectiveness in complex scenarios.
Handling Noisy Environments
In loud settings, like a busy street, focus on visual cues (chest movement) and tactile cues (feeling for breaths) during the 10-second first aid breathing check. Position yourself to block out distractions.
Multiple Victims
In incidents with multiple victims, prioritize those who are unresponsive and not breathing. Perform a quick assess breathing duration for each, then delegate tasks like calling for help to others nearby.Stress Gastritis in Critically Ill Patients – Healthhype
Coordinating with Professionals
When emergency services arrive, provide clear details about your breathing assessment timeframe and actions taken. This helps paramedics continue care seamlessly.
FAQs on Breathing Checks
How long to check breathing?
Check for 10 seconds using the look, listen, feel method to confirm normal breathing or identify the need for CPR.
What if I’m not CPR-trained?
Call emergency services immediately and follow their instructions. Learn basics at HealthHype’s emergency guide.Stress Gastritis in Critically Ill Patients – Healthhype
Can checking take too long?
Yes, exceeding 10 seconds delays critical actions like CPR. Stick to the check breathing time guideline.
What is agonal breathing?
Agonal breathing is irregular gasping, often seen in cardiac arrest. Treat it as no breathing and start CPR.
How to check breathing in infants?
Use a gentle approach, checking for chest movement and faint breaths for 10 seconds. See infant first aid.
What if the scene is unsafe?
Prioritize your safety. Move the person to a safe location if possible before performing an emergency breathing assessment.
Practical Scenarios and Solutions
Understanding the breathing assessment timeframe in context helps you apply it effectively. Here are common scenarios and how to respond.
Scenario 1: Collapsed Adult at Home
Your family member collapses and is unresponsive. Ensure the area is safe, check responsiveness, and perform a 10-second first aid breathing check. If no breathing is detected, call emergency services and start CPR if trained. Review cardiac arrest first aid.
Scenario 2: Child Choking at a Party
A child is choking and can’t breathe. Perform the Heimlich maneuver for children, then check breathing for 10 seconds. If breathing doesn’t resume, start CPR. See choking first aid.
Scenario 3: Drowning at the Pool
After pulling a person from the water, check breathing for 10 seconds. If absent, begin CPR immediately and have someone call for help. Learn more at drowning first aid.
Scenario 4: Hypothermia in Cold Weather
A hiker is unresponsive due to hypothermia. Check breathing for the full 10 seconds, as it may be slow or faint. If no breathing is detected, start CPR and seek help. See hypothermia first aid.
Why Timing Matters
The check breathing time of 10 seconds is not arbitrary. It’s designed to balance accuracy and urgency, ensuring you gather enough information without delaying action. Here’s why timing is critical.
Brain Oxygen Needs
The brain requires a constant oxygen supply. Without it, cells begin to die within minutes. A 10-second evaluate breathing period ensures you identify oxygen deprivation quickly, enabling prompt intervention.
Emergency Response Flow
First aid follows a structured sequence: check safety, assess responsiveness, check breathing, and act (e.g., CPR or calling for help). The breathing assessment timeframe fits into this flow, preventing bottlenecks that could cost lives.
Psychological Benefits
A clear 10-second guideline reduces panic. Knowing exactly how long to check breathing helps you stay focused and confident, even in chaotic situations.
Community Impact of First Aid Skills
Learning how long to check breathing in first aid doesn’t just benefit you—it strengthens your community. Trained individuals create a ripple effect of safety.
Workplace Safety
Certified employees can respond to workplace emergencies, reducing risks and improving outcomes. Encourage your employer to offer first aid training.
Family Preparedness
Teaching family members the first aid breathing check ensures your home is ready for emergencies. Practice together to build confidence.
Public Spaces
In public settings, like parks or malls, your ability to perform an emergency breathing assessment can save strangers’ lives. Your skills make public spaces safer.
Empower Yourself to Save Lives
Mastering how long to check breathing in first aid—10 seconds—is a simple, powerful skill that can save lives in emergencies like cardiac arrest, choking, or drowning. By following the look, listen, feel method, avoiding common mistakes, and preparing for special cases, you’re ready to act with confidence. Don’t wait for a crisis to learn. Visit HealthHype’s first aid hub for more life-saving resources and enroll in a CPR course today. Your knowledge could be the key to someone’s survival. Act now—become a lifesaver!Stress Gastritis in Critically Ill Patients – Healthhype
External References:
- American Heart Association – CPR and First Aid
- American Red Cross – First Aid Training
- Mayo Clinic – First Aid Basics
Heart Stopped – What Happens, Causes, Death, First Aid Treatment